Chairman's Desk
 |
| DR. B.R. GAIKWAD |
| Chairman, CHEMEXCIL |
|
| |
Dear Member-exporters,
I have pleasure to bring to you the 4th issue of the CHEMEXCIL e-Bulletin for the month of August, 2016, which contains the following activities undertaken by the Council and other useful information/Notifications, etc
- Buyer Seller Meets held on 1st Aug. 2016 at Kampala, Uganda.
- Buyer Seller Meets held on 3rd Aug. 2016 at Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
- Seminar on "Customs Procedures for Export and Imports held on 5th August 2016 at Mumbai
- AgriBusiness Global Trade Summit 2016 held at Orlando USA from 17th to 19th Aug. 2016
- Vietnam's Premier International Beauty Show held at Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam from d 18th - 20th August, 2016.
- Achievement of CHEMEXCIL’s Member - Best Exporter in Maharashtra & Brand Ambassador for MSME Award to Vice-Chairman of CHEMEXCIL, Shri Satish Wagh
As you are aware, as part of increasing the membership of the Council as also for the benefit of our member-exporters, we have pleasure to inform you that we had organised FTA Awareness Seminars along with Membership awareness drive at Nagpur on 26th August and at Tarapur on on 30th August, 2016 and another Seminar is also being planned at Dahej on 16th Sept., 2016 in co-ordination with the respective Industrial Associations, all of which are free of cost. Further, we are also planning to give our advertisement in various reputed magazines like Chemical Weekly as part of mobilization of new members.
It is my earnest request to all of you to let us have feedback of your participation in the above events as also your achievements if any in the export field, so as to enable us to include it in our Bulletins being brought out by us every month.
I have also pleasure to inform you that the Ministry of Commerce & Industry has sanctioned MAI Grant in aid of Rs.3.94 crs. under REACH towards reimbursement of 50% of ECHA fee incurred to 69 member-exporters who had registered their 135 substances in the EU during the 2nd Phase of Registration deadline, which was in 2013. The amount will be reimbursed to all concerned shortly, after completing all the procedural formalities.
In order to make this newsletter more useful and informative, the Secretariat looks forward to receiving your valuable feedback and suggestions, if any.
With regards,
Dr. B.R. Gaikwad
Chairman,
CHEMEXCIL
|
BACK |
BUYERS SELLERS MEET ON 1ST AUGUST, 2016 AT KAMPALA, UGANDA
BRIEF REPORT
The BSM at Kampala was followed by the Exhibition in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. This sector was untouched since 12 years and the visit proved to be an eye opener as Indian producers have lot of potential in Uganda. Agrochemicals and Cosmetics are the sectors where India has a lot to offer and the economy of Uganda has great potential and it appeared poised for rapid economic growth and development. A joint venture in terms of manufacturing is an ideal business as trading becomes more expensive since it is a land locked country.
The 31 visitors who attended were from Chemicals, Cosmetics and Agrochemicals sector and had a fruitful meetings with Indian Delegates. The HC Mr. Ramesh Chandra was keen and on setting up the manufacturing units by Indians. He also mentioned that the joint efforts of the Ugandan government and private sector organisations to create an ever-greater economic bond are also expected to gain momentum in the coming years.
The delegates were very much satisfied with their meetings and also made new contacts for enhancing trade between two countries.
 |
| Mr. S.G. Bharadi welcoming His Excellency Mr. Ramesh Chandra
HC of India
|
|
BACK |
BACK |
REPORT ON BUYERS SELLERS MEET ON 3RD AUGUST AT ADDIS ABABA, ETHIOPIA
An excellent inaugural function graced by more than 200 Ethiopians followed by BSM till 3.00 pm.
CHEMEXCIL had organised similar BSM in July 2013 at the same venue. During this BSM 90 Ethiopian business men turned up and at the current BSM in August 2016 CHEMEXCIL BSM witnessed 210 buyers from Ethiopia.
Few companies looking for some important buyers were able to trace their counterparts in Ethiopia after many years which turned to be positive. The Indian delegates were more than satisfactory and congratulated CHEMEXCIL for their commendable performance.
The investment opportunities are vast since Ethiopia is again a land locked country. According to the Indian Companies setting up an unit in Ethiopia will yield more profits than just making Ethiopia a trading partner. After the meetings many companies extended their stay in Addis Ababa and were supposed to visit the Oromia Industrial Park where the industries are located.
Also the business directories containing list of business community in whole of Ethiopia were distributed by Mr. Teddy Tewodros – M/s Olive Trade who was our marketing parter in Addis Ababa. The directory turned out to be of great help to our delegates.
Mr. S.G. Bharadi also made an announcement of CAP INDIA show which is going to take place in Mumbai in March 2016 and invited a delegation from Ethiopia.
All the meetings ended in a fruitful manner with a promise to enhance the trade and give a new height.
|
BACK |
Brief Report on - Seminar on "Customs Procedures for Export and Imports" on 5th August 2016 at Garware Club House, Wankhede Stadium, Mumbai
As a capacity building measure and for creating awareness on “Customs Procedures for Export and Import”, the council had organized this seminar. This event was also supported by ECGC Ltd.
The panelist for the program were-
- Dr. B.R Gaikwad, Chairman- CHEMEXCIL
- Mr. S.G Bharadi, Executive Director - CHEMEXCIL
- Mr. Sudhakar Kasture- Director- Helpline Impex Pvt Ltd.
- Ms. Padmavathy R, GM- ECGC Ltd and other officials of ECGC
Dr. B.R Gaikwad- Chairman CHEMEXCIL gave his welcome address and advised the participants to benefit from the expertise of the speakers and interact with them.
The key speaker - Mr. Sudhakar Kasture, Director, Helpline Impex Pvt Ltd covered topics such as Understanding Import/Export documents, Process of filing of EDI Bill of Entry/ Shipping bill/ Bill of Export, Understanding classification & importability/ Exportability of item, Process of Valuation, Rules for valuation of Imports & Exports, Process of assessment & clearance of goods under Advance Auth./EPCG Authorisation/Duty Credit Scrips.
ECGC’s representatives also made presentation on export credit risk insurance policies and interacted with the participants.
The event attracted good response with participation of around 45 members. The participants interacted with the speakers and also got clarifications on their queries.
| Glimpses of the Seminar on Customs Procedures for Export & Import |
 |
| Dr. B.R Gaikwad Chairman welcoming the participants
|
|
BACK |
Brief Report on - AgriBusiness Global Trade Summit 2016, Orlando USA
As an export promotion measure, the Council has participated in the Agri Business Global Trade Summitheldduring 17th– 19th August, 2016 at Caribe Royale Hotel, Orlando, Florida. The said project is sanctioned under MDA.
The AgriBusiness Global Trade Summit is a global sourcing event for crop protection and plant health products. It’s core attendees included more than 140 exhibitors from China, India, the United States, EU and Southeast Asia and offer both technical-grade and formulated crop protection products, bio pesticides, bio stimulants, micronutrients, PGRs and more. The show attracts visitors not only from USA but also various neighbouring Lac countries.
In order to provide platform to CHEMEXCIL members and also to assist our members to explore the agrochemicals market potential in USA and surrounding areas, CHEMEXCIL had organised participation in this event by booking 99 sqm space. Total 11 members showcased their products under the umbrella of CHEMEXCIL.
The show attracted around 750 registrations by business delegates from various companies in USA, Mexico, Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Guatemala etc.
The member-participants of CHEMEXCIL had fruitful interaction with business delegates who visited their stalls and were satisfied with the response as these interactions might give them foothold in USA as well as high potential LAC markets.
| Glimpses of the Show |
 |
| Mr. Deepak Gupta Dy. Director CHEMEXCIL with a Stall Holder
|
|
BACK |
Vietnam’s Premier International Beauty Show, At Saigon Exhibition and Convention Centre (SECC),
Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam Dated 18th– 20th August, 2016
CHEMEXCIL has participated in "Vietnam's Premier International Beauty Show - VIETBEAUTY" held from 18th - 20th August, 2016 at Vietnam. The purpose of this exhibition was to create a positive brand image of Indian cosmetics products in Vietnam.
The exhibition was organized at at Saigon Exhibition and Convention Centre (SECC), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. andCHEMEXCIL took part in this event along with 16member exhibitors. There were prominent visitors from around region countries.
Mr. Prafulla Walhe, Dy. Director was deputed to lead the exhibition delegation.
The emphasis of VIETBEAUTY waslied on the following main / business sectors: Detergents and cleanser products, skin and hair care products, perfumes, eau de cologne and spray, hair colours, cellulose and hygienic products, fresheners, home hygienic products,raw materials, tools and accessories for hair salons, trade and consulting services.
 |
| Mr. Prafulla walhe Dy. Director CHEMEXCIL along with Vietnam VIP’s and UBM Organiser at CHEMEXCIL stall at Vietnam Beauty. |
|
BACK |
Seminar on "CHEMEXCIL Membership awareness and Export benefits at Nagpur dated 26.08.2016"
 |
| From Left Shri.SudhkarKasture guest speaker, Shri.AtulPande President VIA, Shri.S.G. Bharadi Executive Director Mr. Prafulla Walhe, Dy. Director CHEMEXCIL, Dr. SuhasBuddhe Hon. Secretary VIA
|
CHEMEXCIL along with VIDARBHA INDUSTRIES ASSOCIATION conducted seminar on "CHEMEXCIL Membership awareness and Export benefits at Nagpur on 26th August 2016 at VIDARBHA INDUSTRIES ASSOCIATION, FIRST FLOOR UDYOG BHAWAN, CIVIL LINES, NAGPUR 440001.
The very objective of this seminar was to create CHEMEXCIL awareness and educate the members on various aspects of Export Incentives as per Foreign Trade policy 2015-2020.
The Guest Speaker for the seminar was Mr. SudhakarKasture, Consultant & Director, Helpline ImpexPvt Ltd and Mr. S.G. Bharadi, Executive Director CHEMEXCIL, Mr. Prafulla Walhe Dy. Director, CHEMEXCIL. Following topics were covered during the seminar Export Incentives as per Foreign Trade Policy 2015-2020, Export incentives schemes, details about CHEMEXCIL and its structure, Importanceof CHEMEXCIL to Chemical Sector, details on CHEMEXCIL membership.
Total 50-members from Nagpur and surrounding region attended this seminar
|
BACK |
Seminar on "CHEMEXCIL Membership awareness and Export Incentives atTarapur dated 30.08.2016"
CHEMEXCIL along with North Konkan Chamber of Commerce & Agriculture (NKCCA) conducted seminar on "CHEMEXCIL Membership awareness and Export incentives at Tarapuron30th August 2016 at TIMA Auditorium, Tarapur MIDC, Dist. Thane, Maharashtra.
The very objective of this seminar was to create CHEMEXCIL awareness and educate the members on various aspects of Export Incentives as per Foreign Trade policy 2015-2020.
The Speaker for the seminar was Mr. Prafulla Walhe, Dy. Director CHEMEXCIL along with Mr Deepak Chaudharifrom Indus group of company, Dr. Rajiv Churi, President NKCCA and Mr. MrMilindPatil. Following topics were covered during the seminar Export Incentives as per Foreign Trade Policy 2015-2020, Export incentives schemes, details about CHEMEXCIL and its structure, Importance of CHEMEXCIL to Chemical Sector, details on CHEMEXCIL membership.
Total 55-members from Tarapur and BoisarMIDC region attended this seminar
|
BACK |
CHEMEXCIL MEMBERS ACHIEVEMENT
 |
| Shri. Satish Wagh vice chairman CHEMEXCIL Felicitated ‘Best Exporter in Maharashtra’ and ‘Brand Ambassador for MSME’ Award presented by the Hon’ble Governor of Maharashtra, Shri C. Vidyasagar Rao at the ‘SME Manufacturers & Exporters Summit’ organised by the SME Chamber of India and Maharashtra Industrial & Economic Development Association on 19th Aug. 2016 at Hotel Sahara Star Mumbai in the presence of ShriSubhash Desai, Hon’ble Minister of Industries, Govt. of Maharashtra and Shri Deepak Kesarkar, Minister of State for Finance, Rural Development & Planning, Govt. of Maharashtra.
|
Will GST help India ramp up exports?
The passage of the Constitution (122nd amendment) Bill, 2014, on Wednesday allows for the launch of the Goods and Services Tax (GST), a unified and pan-national tax structure. GST will create a common domestic market, remove distortions arising out of a multiplicity of levies and rates, and foster efficiency by minimizing the cascading effect of taxes in the manufacturing chain. GST will also have a beneficial impact on India’s economic diplomacy, including foreign trade.
The GST fits nicely into the Modi government’s drive to improve ease-of-doing business in the ‘Make In India’ campaign. Manifold taxes, with differential rates in different states, created hurdles for the smooth conduct of business and added costs at every stage, frustration foreign investors. Foreign Investment decisions and the expected rate of return from projects often suffered due to these distortions, occasionally even deterring fresh investment plans. Most global value chains, with the exception of Foxconn, have avoided investing in India because of regulatory and bureaucratic tangles, especially those related to the multi-layered tax regime.
The successful implementation of GST will reverse this, helping to attract new investments especially from global value chains which often aggregate inputs from different constituencies.
The other immediate beneficiary will be Indian exports which have long suffered from lack of international competitiveness due to differential taxes and the energies expended on complying with the complex tax labyrinth. A 2010 report from National Council of Applied Economic Research had found that eliminating cascading taxes on exports could increase GDP growth by 0.9-1.7 per cent.[1]
For instance, a garments manufacturer and exporter has to depend on multiple suppliers of inputs – finished cloth (processed and dyed), threads, buttons, zips, sewing machines, ironing products, packaging, labels – for producing his finished good. These suppliers in turn, source raw materials from multiple sources, located in multiple locations, each party paying multiple taxes in different tax jurisdictions. At each stage, goods get delayed in transit for assessment and payment of varied levies – sales tax, octroi, excise, service tax. This fosters inefficiency and adds costs to each additional layer for the exporter. In addition, with each state legislating separate laws, meant that exporters couldn’t claim full set-off on the free-on-board price, rendering exports uncompetitive.
GST will alleviate this. The Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) for 2015-20 says: “The simplification and harmonization of the indirect tax regime of the country will reduce the cost of production and lead to a seamless, integrated Indian market, thereby making Indian trade and industry more competitive.”[2]
The benefit to services exports will become clearer in the next few weeks, but right away, the travel, tourism and hospitality sector is a clear winner because of its dependence on a wide spectrum of vendors and suppliers.
As the implications and impact of this simplifiying legislation starts to make itself apparent and the GST’s advantages for incoming foreign investment and out-going exports gain momentum, it will add veracity to Prime Minister Modi’s on-going economic diplomacy efforts.
(Ref. http://www.zeebiz.com/india/in-depth-will-gst-help-india-ramp-up-exports-4570# dated 03.08.2016)
|
BACK |
DIPP secretary urges industry to back government to achieve ease of doing business
 |
| New Delhi: Ramesh Abhishek, Secretary, DIPP, Ministry of Commerce and Industry, on Friday urged the Indian industry to actively engage, support and cooperate with the government to achieve ease of doing business and attract investments into the country. |
Addressing a FICCI conference on 'Ease of Doing Business: Distance to Destination', Abhishek said that the Government was working on various spheres to accelerate the economic growth and had successfully brought about effective changes in many Acts and policies. Now incorporating a company meant less paper work and easier process, application of PAN was online besides services such as EPFO and ESI but the industry needed to provide constant feedback to the government on the efficiency and effectiveness of the systems to plug the gaps that still existed.
Abhishek suggested that FICCI should undertake a study which clearly states the areas where government intervention could facilitate business. The study should highlight the best practices of other countries in those areas and how India could adapt those practices to suit its requirements.
Abhishek said that the states are competing with each other to attract investment by way of simplifying their processes and making their systems online. The 340 Action Plan has allowed states to clearly showcase their achievements and improvement areas on various parameters, making the process of ranking the states for ease of doing business transparent.
On the occasion, FICCI Trilegal Knowledge Paper 'Ease of Doing Business: Distance to Destination' was released by Abhishek.
In her keynote address VijayaSampath, Chairperson, FICCI Corporate Laws Committee, said that the World Bank ranks a country's ease of doing business on three parameters - procedure, time and cost. Hence to improve the ease of doing business ranking, the government needs to facilitate the private sector. For this the government needs to make helpful interventions by way of formulating quantitative and quality regulations that would bring a right balance to the environment of business. She added that effectiveness and efficiency were the two major imperatives that needed to be embedded in the system.
Sidharth Birla, Past President, FICCI and Mentor, FICCI Corporate Laws Committee, said that with ease of doing business there was a need to bring about competitiveness in Indian industries and services sector. He added that FICCI has been relentlessly working on various aspects of economy with different Ministries and Departments of the Government and regulatory bodies in the country such as SEBI, CCI to improve ease of doing business.
In this context, Birla pointed out that FICCI was the first to advocate the need to ensure that norms for doing business should be so designed as to enable India to be counted amongst the first 50 countries in the World Bank's Ease of Doing Business ranking.
In his presentation on FICCI Trilegal paper, Harsh Pais, Partner, Trilegal, said that the paper has focused on areas where government intervention has significantly contributed to ease of doing business. The four key areas discussed in the paper are Corporate governance; Solving insolvency; Anti-corruption enforcement; and Amended Arbitration Act.
In his concluding remarks Dinesh Chandra Arora, Secretary, Institute of Company Secretaries of India, said that in the last two years the government has put in place many transformative polices and processes. Now the time is to effectively implement the various initiatives and policies to attract investment and improve ease of doing business. He added that simplified processes, single window clearances and online registrations were some of the aspects that would make it India an easy business destination.
A Didar Singh, Secretary General, FICCI, said that with the landmark GST reform now moving ahead doing business in India would be greatly facilitated. The environment in which the business operates needs to change and GST would be playing a key role in bringing about this change.
(Ref. http://www.newsx.com/business/37177-dipp-secretary-urges-industry-to-back-government-to-achieve-ease-of-doing-business dated 05.08.2016)
|
BACK |
DGFT assures transparent, robust process to boost exports
Additional Director General of Foreign Trade Sonia Sethi today reassured the micro small and medium enterprises (MSME) sector that her office is working to improve governance and transparency with a time-bound schedule of services to ensure exports pick up in the coming months.
Addressing the open house meet organised by the World Trade Centre Mumbai and All India Association of Industries Sethi said: "My team is pulling up its socks on all issues faced by industry and the potential entrants in the MSME segment. The MSME clusters are our priority in export promotion."
As per the Foreign Trade Policy 2015-2020, India's exports is targetted to jump from USD 465.9 billion to USD 900 billion by 2020 - i.E.From a share from 2 to 3.5 per cent.
Sethi also assured the exporters that she would soon convene a meeting of the committee on quality complaints and trade disputes.
"We have a comprehensive basket of deliverables and our effort is to facilitate and resolve difficulties faced by exporters. Large part of our systems is now online," she explained.
(Ref.http://www.business-standard.com/article/pti-stories/dgft-assures-transparent-robust-process-to-boost-exports-116080801720_1.html date 09.08.2016)
|
BACK |
SEZs must register with council to avail duty drawbacks, exemptions
NEW DELHI: The government has made it mandatory for all special economic zones to obtain certificates from the Export Promotion Council for SEZs and EOUs if they want rebates like duty drawbacks.
"The unit or the developer including co-developer shall obtain a registration-cum-membership certificate for availing exemptions, drawbacks and concessions," the commerce department said in a recent diktat.
Besides making SEZs accountable for the exemptions they get, the move would also help in policy making as their feedback can be considered, officials said.
At present only 800 out of 4,100 operational SEZ units are registered with the export promotion council, making it difficult to streamline the sector. Whenever the government seeks feedback on important issues such as budget, foreign trade policy or even tax policy, it doesn't get a complete picture because views of all the SEZs that are not registered are not covered, officials said.
AnandGiri, officiating deputy director general at Export Promotion Council for SEZs and EOUs (EPCES), said, "At present, SEZs are members of other product specific councils. When they face any problem they write to their council that then take it up with ministry concerned such as textiles, steel and IT, among others, instead of writing to SEZ division or to EPCES."
He said, "So, with this change in SEZs, they at least can be enrolled with us and the government can get authentic and urgent feedback on any issue regarding the SEZ scheme... SEZs will also get a proper platform to raise their issues."
The development comes even as the government is looking to boost investor interest in SEZs that are deemed to be foreign territory for purposes of taxes, duties and trade, and give a big push to exports.
(Ref. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/policy/sezs-must-register-with-council-to-avail-duty-drawbacks-exemptions/articleshow/53679536.cms dated 13.08.2016)
|
BACK |
Stringent norms to minimise chemical accidents
NEW DELHI: Concerned over rise in accidents in chemical installations, union environment ministry has decided to review over two-decade old laws dealing in hazardous chemicals so that effective enforcement of regulations in chemical industry in ensured and chemical accidents are minimised.
The ministry has decided to amend two sets of laws that regulate the manufacturing, use and handling of hazardous chemicals. These include – Manufacture, Storage and Import of Hazardous, Chemical (MSIHC) Rules, 1986 and Chemical Accidents (Emergency Planning, Preparedness and Response), (CAEPPR) Rules, 1996.
The need was felt as according to ministry, a number of accidents in chemical industry installations in the recent past have brought into focus the need to review the missing gaps in aforesaid rules so that effective enforcement of regulations in chemical industry in ensured.
“There is an urgent need for amendment of the aforesaid rules in line with the existing needs for minimization or control of chemical accidents,” it further said.
The ministry has now sought inputs from all concerned stakeholders and common public for reviewing the laws.
India has witnessed the world’s worst chemical disaster Bhopal Gas Tragedy in the year 1984. It was the most devastating chemical accident in history, where over thousands of people died due to accidental release of toxic gas Methyl IsoCyanate (MIC).
The numbers have been rising since then.
Around 1500 fatal and non-fatal injuries in chemical factories, including pharmaceuticals companies, were reported in 2014, according to Minister of Labour and Employment BandaruDattatreya. The National Disaster Management Authority says that 130 significant chemical accidents were reported in India in last one decade, which resulted into 259 deaths and 563 number of major injured.
The environment ministry is the nodal ministry for chemical (industrial) accidents and its task to implement the two laws. MSIHC prevents major chemical accidents arising from industrial activities and limit the effects of chemical (industrial) accidents and CAEPPR Rules, 1996 provides the statutory backup for Crisis Management setup.
These Rules prescribe criteria for identification of Major Accident Hazard (MAH) installations and all districts with such installations are required to establish crisis management groups.
In addition, as prescribed by the MSIHC Rules, 1989, the occupiers of the Major Accidents Hazard (MAH) Unit are responsible for preparation of an on-site Emergency Plan: and the Chief Inspector of Factories in consultation with District authorities are required to prepare off-site emergency plans as well.
(Ref. http://www.newindianexpress.com/nation/Stringent-norms-to-minimise-chemical-accidents/2016/08/15/article3580995.ece dated 15.08.2016)
|
BACK |
National Committee on Export Import Facilitation Constituted to implement WTO Agreement
New Delhi, Aug 16 (KNN) The Finance Ministry has recently notified constitution of the National Committee on Trade Facilitation as required under the WTO agreement.
The objective of trade facilitation is expediting movement, release and clearance of imports and exports including goods in transit. Under the agreement there are also provisions for customs cooperation.
The tasks before the national committee is to finalise a trade facilitation plan, develop an programme for training of exporters and importers and suggest necessary legal changes required.
Under the National Committee there will be a Steering Committee to study the gap in compliance of the WTO guidelines and also suggest changes required in this regard. Monitoring of implementation of the WTO guidelines on trade facilitation will also be the responsibility of the Steering Committee.
The MSME sector has found representation in the steering committee through FISME, the leading federation of MSME Associations.
As per the mandate of WTO, every signatory nation of the Trade facilitation Agreement has to adequately publicise the procedures, fees etc. for international trade, make all information available through internet, set up specific enquiry points for international traders.
Following the guidelines, the foreign trade policy of 2015 – 2020 has incorporated online submission of documents, paperless transfer of cases among Government departments etc.
It is a different issues that a large number of MSMEs complain of mis- function of the IT system and delay in clearances of documents and merchandise by one reason or other.
Trade facilitation is crucial for the MSME sector, who contribute nearly half of the India’s total export. As MSMEs cannot afford specialist trade consultants, they almost always suffer delays and cost escalation in foreign trade due to unhelpful attitude of the officers, complicated procedures and illogical conditions.
It is expected that the Trade facilitation bodies will also look into these issues.
The Committee to be headed by the cabinet Secretary and with members from apex trade bodies and chambers are expected to implement the Trade Facilitation Agreement in both letter and spirit.
Commenting on the continuous drop in India’s export, Mr. Anil Bhardwaj, Secretary General, FISME, commented “ Today 80% of the international trade is linked to global value chains, where inputs are imported from most competitive country, only those operations are carried out, where the importer has competitive advantage, and the ‘semi-finished’ product is re-exported to a buyer offering best terms”.
‘Under this environment, both the import and export should be hassle free and any bottleneck or delay will take the order away to another shore, as happened in the case of Textiles’, he commented.
With such a scenario, the importance of Trade Facilitation, which in simpler terms is easy and prompt imports and exports at minimum cost, cannot be overemphasised.
Whether the National Committee under the Cabinet Secretary will be able to achieve the same to materialise the vision of Our Prime minister of ‘Make in India’ is the moot question of MSME fraternity.
(Ref. http://knnindia.co.in/news/newsdetails/msme/national-committee-on-export-import-facilitation-constituted-to-implement-wto-agreement dated 17.08.2016)
|
BACK |
National Committee on Export Import Facilitation Constituted to implement WTO Agreement
The commerce ministry has relaxed certain norms to promote outbound shipments and manufactured products from export-oriented units (EoUs), software technology parks of India (STPIs) and electronic hardware technology parks (EHTPs).
The norm of mandatory warehousing requirement for EoUs and software and electronic hardware technology parks has been done away with.
The Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) has also eased rules for the existing EHTP and STP units to avail tax exemptions in the case of conversion or merger of EoU and vice versa.
In a notification, the department said an EoU, which is into agriculture, aquaculture, horticulture and poultry, might be permitted to remove specified goods in connection with its activities for use "outside the premises of the unit".
Earlier, it was allowed only for outside the bonded area. DGFT has said this in a notification, amending the foreign trade policy (2015-20).
The EoU scheme, which was introduced in December 1980, had allowed manufacturing units in export processing zones to enjoy 100 per cent tax exemption on profits from overseas sale and duty-free import of raw material.
As the scheme had a sunset clause, the tax benefits were stopped from March 2010. This scheme was utilised by small and medium enterprises to set up their units for the purpose of exports.
Later, a committee had suggested steps, including tax incentives, to revive these units.
The decision takes on significance as the country's exports, after rising for the first time in 19 months in June, shrank again in July. It contracted 6.84 per cent due to the decline in shipments of engineering goods and petroleum products.
(Ref. http://www.business-standard.com/article/economy-policy/commerce-min-eases-rules-to-promote-exports-116081700050_1.html dated 17.08.2016)
|
BACK |
Bulk cargo movement facility denied for all commodities
 |
| File – Cargo trucks heading to Nepal have been left stranded at Nautanwa of Uttar Pradesh for over a month. Photo: RSS |
| |
Indian government has shown reluctance to provide bulk cargo movement facility for Ms-Billet and chemical fertilisers. Sending comments on the proposed letter of exchange (LoE) titled ‘Process Simplification and Additional Route’, the Ministry of Commerce, India, has given consent only for coal and cement/clinker.
Nepal had proposed to the Indian government to provide bulk cargo movement facility for Ms-Billet, chemical fertilisers and cement/clinker to the rail heads of Nautanwa (Bhairahawa) and Jogbani (Biratnagar) from Kolkata some two years back seeking support from the southern neighbour for the industrialisation of the country.
This facility was sought to minimise the cost of transport logistics, so that industrial production in Nepal could be competitive. The high cost of production caused by various factors including high transport logistics has stalled industrialisation process in the country.
In the meantime, the government of India has opened Visakhapatnam Port as another gateway for Nepal’s third-country trade. In this context, the country has sought transit facility for bulk cargo movement from both Kolkata and Visakhapatnam Port, which will save time and logistic costs for traders importing commodities such as chemical fertilisers, cement, iron ore and coal.
The Indian government principally agreed to provide transit facility for bulk cargo movement but did not provide the facility for all the commodities proposed by Nepal.
As per officials at Ministry of Commerce, the government is again preparing to send the draft LoE with justifications.
Bulk cargo generally refers to goods ferried in open railway wagons. That is cost effective and also saves time than when cargoes are ferried in sealed containers. Currently, bulk cargoes are entering Nepal via Kolkata-Raxaul (Birgunj) route and unloaded at Inland Clearance Depot, Birgunj, before they are transported to other parts of the country, which has been increasing cost of transport within the country and congestion in the only rail-linked ICD.
As per Rajan Sharma, transit and transport committee chairman of Federation of Nepalese Chambers of Commerce and Industry, transit facility for bulk cargo movement will be instrumental in lowering logistic cost of ferrying various goods and also traffic on Kolkata-Birgunj route would come down, which will reduce travel time.
The country’s domestic distribution system could also be improved, and basically industries located in Bhairahawa and Biratnagar area will also benefit, as per Sharma. This is because goods, such as chemical fertilisers, cement, iron ore and coal, are currently being distributed throughout the country from Birgunj. Once the two new trading routes for bulk cargoes are opened, Biratnagar will start serving the demand of eastern Nepal, while Bhairahawa will emerge as the distribution hub for goods in the country’s western part.
Attempts made by The Himalayan Times to reach concerned officials of the Embassy of India in Kathmandu to verify the information were not fruitful. But traders have said that Indian government is reluctant to provide the facility for more commodities because when bulk cargoes are transported in open containers, it tends to pose security threat and also causes pollution.
(Ref. https://thehimalayantimes.com/business/bulk-cargo-movement-facility-denied-commodities/ dated 18.08.2016)
|
BACK |
Government initiates exercise to update 'Make in India' action plan
 |
According to DIPP Secretary, commerce and industry minister as reviewed the action plan with all departments and has also discussed it with all stakeholders, including industry associations.
Government has initiated an exercise to revise the 'Make in India' action plan, a top official said on Wednesday.
Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion (DIPP) Secretary Ramesh Abhishek said that the commerce and industry ministry has reviewed the action plan with all departments and has also discussed it with all stakeholders, including industry associations. Based on the meetings, "now we have a tentative revised plan which has been now proposed to various ministries and departments. We have requested them to examine the inputs received from the industry", he said.
"We have requested them to see whether, how and in what manner these Make in India action plans can be revised. We have also decided to do a kind of reality check on what has been achieved so far in the last two years," he told reporters here. The 'Make in India' programme was launched in September 2014 with an aim to make the country a global manufacturing hub and attract investments. In December 2014, the government came out with short and medium term action plans for all 25 thrust sectors under the programme.
"Since then we have been reviewing regularly the progress made and in the last three months, we have reviewed this again with all the ministries and department concerned," he said. He added that the DIPP has also started a dashboard from April 1 in which monitoring is being done by the department concerned. "They are uploading their progress on this and we are getting now the real time information about the achievements of the departments against their short term as well as their medium term targets and goals of the Make in India programme," he added.
He said that in the last three months "we have been reviewing with all the departments, not only what has done so far but also what more needs to be done because as the plans were made in December 2014, naturally there are many things that needs to be done". Many of the action plans have already been achieved, he added.
Further he said that the DIPP has prepared a document compiling the progress under Make in India initiative. To start with, he said, today the DIPP is releasing the document of the food processing sector and "we are doing this exercise for all the sectors and the work is in progress". The 25 key sectors identified under the programme include automobiles, auto components, bio-technology, chemicals, defence manufacturing, electronic systems, food processing, leather, mining, oil & gas, ports, railways, ports and textile.
(Ref. http://www.dnaindia.com/money/report-government-initiates-exercise-to-update-make-in-india-action-plan-2246279 dated 18.08.2016)
|
BACK |
DIPP Takes Over from Department of Finance to Set Credit Fund Norms
Startups are one step closer to being able to borrow money, with the Department of Industrial Policy & Promotion (DIPP) given charge of framing guidelines for a credit guarantee fund for them, reported Economic Times.
Department of Industrial Policy & Promotion was established in the year 1995, and in the year 2000 Department of Industrial Development was merged with it.
“EARLIER, THE MATTER WAS BEING DEALT WITH BY THE DEPARTMENT OF FINANCE. WE HAVE STARTED THE WORK AND IT SHOULD BE FINALISED BY SEPTEMBER. THE CREDIT GUARANTEE FUND WOULD HELP IN THE FLOW OF VENTURE DEBT FROM THE FORMAL BANKING SYSTEM,” A SENIOR GOVERNMENT OFFICIAL SAID.
DIPP is working under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India. This department is responsible for formulation and implementation of promotional and developmental measures for growth of the industrial sector, keeping in view the national priorities and socio-economic objectives.
While individual Administrative Ministries look after the production, distribution, development and planning aspects of specific industries allocated to them, Department of Industrial Policy & Promotion is responsible for the overall industrial policy.
DIPP works consciously and dedicatedly for positioning India amongst the top industrial countries of the world in a relatively shorter time frame. It create enormous opportunities for investment in sustainable industrial activities and open up employment avenues for enhancing the quality of life of the common man.
(Ref. http://techstory.in/19082016-dipp-takes-department-finance-set-credit-fund-norms/ dated 19.08.2016)
|
BACK |
Backlog in issuing of export obligation certificates to be cleared in 6 - 8 months: ADGFT assures MSME exporters
Bengaluru, Aug 19 (KNN) The backlog in issuing the export obligation certificates will be cleared in six to eight months’ time, Vijay Kumar, Additional Director General of Foreign Trade assured the MSME exporters.
Addressing a workshop on Export Obligation & EPCG Guidelines, Procedures and the Foreign Trade Policy and the Various Schemes organized at KASSIA on Thursday, ADGFT clarified that job works done in EOUs/SEZs would be accounted towards the export obligation turnover.
He said the EPCG licensee will also get a condonation of up to 20 per cent in meeting the yearly obligation in case of economic slowdown in the destination market.
Vijay Kumar outlined the many initiatives launched by the Ministry of Commerce to encourage and facilitate growth and development of exports in the face of steep decline in exports in the last two years.
He particularly mentioned the NirayatBandhu Scheme specially aimed at new and prospective exporters to introduce them to the policy and procedures from which to benefit while making exports.
He said the IEC is now issued online and new schemes like MEIS have been introduced revamping old schemes cutting down layers of procedures and delays for the benefit of the exporters.
The Bangalore Office of the DGFT will organize six programmes in different parts of the State this year aimed at educating and informing the business community including the MSMEs, he said adding that the Bangalore Office is now freely accessible to trade and industry every day where they can come and settle their problems by discussing issues face to face.
He hoped all these measures would result in giving a fillip to exports from this region and the country.
A Padmanabha, President, KASSIA emphasized the need for working in close partnership between the industry and the DGFT.
He said that MSEs now face open markets globally in which they will have to compete and survive and the best way to do that is by learning and understanding the policies and procedures of the beneficial schemes.
He hoped that the workshop would result in better understanding of export procedures and policies and further closer relationship between the stakeholders to derive the best out of the various schemes. (KNN Bureau)
(Ref. http://knnindia.co.in/news/newsdetails/sectors/backlog-in-issuing-of-export-obligation-certificates-to-be-cleared-in-6-8-months-adgft-assures-msme-exporters dated 19.08.2016)
|
BACK |
Govt. fast-tracks National Trade Policy to facilitate ETCA
In parallel with the ongoing preliminary discussions on the Indo-Sri Lanka Economic and Technology Cooperative Agreement (ETCA), the Government has appointed a high level, seven-member committee to formulate a national trade policy in keeping with the demands of professional bodies.
“The first draft of that policy will be submitted to the Government for consideration and will be further shaped by amendments, before it is shared with professional organisations and trade unions, while an initial note prepared by the head of the committee is under discussion” Development Strategies and International Trade Ministry Secretary ChandanieWijewardena told the Sunday Times.
The committee, headed by Dr Ravi Ratnayake, an international economist specialising in economic development, trade and investment, also includes Senior Presidential Advisor, DrSarathRajapathirana; SubhashiniAbeysinghe, Senior Analyst and Head of Economics at Verité Research, an independent multi-disciplinary think tank; Additional Secretary of the ministry, W.D.S. Gunasinghe; Director- Dept of Trade and Investment of Ministry of Finance, V. Vimalarajah; Ministry of National Policies and Economic Affairs, Representative, U.G. Ratnasiri and Central Bank Assistant Governor, K.D. Ranasinghe.
Minister Malik Samarawickrama has instructed the committee to prepare the draft, as the government, in its initial steps to start negotiations on the proposed ETCA agreement with India, wants to put a national trade policy in place before finalising the pact. Once the complete draft is prepared, he is expected to share it with party leaders, trade unions and professional bodies for their opinions.
The ministry has appointed at least nine subcommittees on various subjects such as investment, international trade and economic services that are core to a developing economy.
Professional bodies, the business community and trade unions agitated early this year against the proposed ETCA agreement with India, claiming that, without a solid national trade policy in place, negotiating trade agreements and Free Trade Agreements (FTA) with foreign countries would put the economy in a difficult mode.
Meanwhile, India’s Minister of State for Commerce, NirmalaSithraman is scheduled to visit Colombo this week, following an invitation extended by Minister Samarawickrama when he visited India last month.
“The visit is about common bilateral trade relations between the two countries and not necessarily focused on ETCA. The two parties are expected to share their thoughts on the outline of the agreement which was discussed recently,” MsWijewardena said.
Earlier this month, an Indian delegation led by the Joint Secretary of India’s Commerce Ministry Bhupinde Singh Bhalla, held preliminary talks on ETCA, where the two parties shared the outline framework of the agreement and agreed to develop from there.
(Ref. http://www.sundaytimes.lk/160821/news/govt-fast-tracks-national-trade-policy-to-facilitate-etca-205683.html dated 21.08.2016)
|
BACK |
Reshaping India’s trade policy
Trade data for June 2016 brought cheers as India’s merchandise exports showed positive growth after 18 excruciating months. However, in their effort to take exports to the next level, India’s trade policymakers face four major challenges: How to encourage foreign investments, obtain a balanced outcome of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs), improve ease of doing business, and reduce dependence on export promotion schemes?
Coincidentally, all four concerns can be addressed by just one action: carrying out a selective reduction in basic custom duties. As the past reductions confirm, it will not lead to the doomsday scenario of domestic industry being wiped out and widespread unemployment. Also, duties are no more the import barriers they used to be. While the earlier 100 per cent tariffs could stop imports altogether, today’s 10 per cent cannot. That is why the international trade game has already shifted to non-tariff barriers such as product standards. We are slipping in this game and must brace up fast.
Benefits of low duty
Studies show that when duties fall below tipping point, there is large and non-linear increase in trade. Therefore, the world has decisively moved towards a low import duty regime. Simple average import duties on industrial goods in Canada, Japan, Australia, the US and the EU are 2.3, 2.6, 3.0, 3.1 and 4.2 per cent respectively. The top six Asean countries have already implemented zero rates on 99 per cent of tariff lines on intra-Asean trade. About 70 per cent of world trade takes place duty-free thanks to the WTO and numerous FTAs. In India, trade and duties seem to be inversely related. Between 1991 and 2016, while India’s merchandise trade (exports and imports) rose from $37 billion to $642 billion, average duties came down from 128 per cent to 10.2 per cent. However, selective reduction in basic custom duties will address major trade policy concerns.
Low duties encourage foreign investment. Large global manufacturers develop supply chains across countries. Since the complex production process requires goods to cross borders several times at different stages, any duty charged has a cascading and accumulative effect. This makes high duty locations an unattractive destination for investment. Trade facilitation and duty reduction are the first steps for enhancing foreign investment potential and increasing trade.
Low duties make FTAs more balanced. At the most basic level, FTAs allow zero or concessional duty imports from partner countries and hence the first visible impact of any FTA is the loss of customs revenue. Concerns are regularly raised over the higher revenue losses for India compared to partner countries, even as the actual imports under FTAs are still far below the potential. But that’s a no-brainer. A country with 10 per cent duty will lose more than a country with 2 per cent duty. There are other problems as well.
A country with higher import duties also ends up giving more market access and buys less goods from the cheapest sources compared to the FTA partner country.
Consider the case of two countries, H with an average tariff of 20 per cent and L with an average tariff of 2 per cent. H and L agree to eliminate tariffs through an FTA. The exporters from L would export more to H as they get a huge 20 per cent price advantage over others. Country H would suffer a higher revenue loss due to the steep tariff reduction, while its consumers may not benefit from the decrease in prices as exporters from L would keep most margins. Domestic producers of H would suffer the most. One, they have to compete with zero duty imports of finished goods from L; and two, they may have to import raw materials from the non-FTA partner country at high duty which will make their products uncompetitive.
Less cumbersome rules
Low duties will make the duty structure simple and improve ease of doing business. High duties have necessitated the granting of many customs duty exemptions that vary according to product, user, or intended use. These have made India’s current tariff structure complex and difficult to implement. High duties also lead to evasion, litigation and corruption.
Low duties will simplify export schemes. To make exports competitive, the Foreign Trade Policy allows duty-free import of raw materials and capital goods under the duty exemption schemes. These schemes have become complex because of the need to ensure that such imports have indeed been used for export production and not for sale in domestic market. The drawback scheme that refunds the duties paid on inputs costs about ₹40,000 crore annually. The higher the duties, the more the outgo, and higher the allure to take more than is due. So, there is always the issue of a few firms importing duty-free and filing fraudulent drawback claims, keeping the Directorate General of Foreign Trade enforcement wing or the Directorate of Revenue Intelligence on their toes. Once duties come down, many such schemes will lose relevance.
Alternative duty structure
The following plan can be debated for a nuanced reduction in basic custom duties without disturbing the revenue collection target. While the share of all types of custom duties in tax revenue is 14 per cent, the share of basic custom duty is 4 per cent or ₹65,000 crore. One, identify 5 per cent of industrial tariff lines as strategic and retain the current level of duty on these. These may include items on which we wish to invite FDI for manufacturing. Most countries have done this at some point. Developed countries like US and EU even today retain high duties on labour intensive products exported by developing countries.
Two, reduce duties on most raw materials and intermediate goods. A look at duties imposed across tariff lines throws interesting insights. India collects more than 85 per cent of basic custom duty from less than 10 per cent of tariff lines. The bottom 60 per cent tariff lines contribute to less than 3 per cent of revenue. Within this framework, India can consider zero duty on all raw materials and intermediate goods. For most of the remaining industrial products, India may move to 5 per cent duty in next 3 years.
Strategic duty reduction will be an important step in moving towards a modern trade policy regime needed for high growth in trade and investment.
The writer is from the Indian Trade Service. The views are personal
(Ref. http://www.thehindubusinessline.com/opinion/reshaping-indias-trade-policy/article8894080.ece dated 24.07.2016)
|
BACK |
Trade impact of Brexit on India: Opportunities and negatives
India and EU have been negotiating the Bilateral Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA) since 2007, covering trade in merchandise, services, and investment. This is yet to reach a conclusion.

The United Kingdom (UK), European Union’s (EU) second-biggest economy, voted by a margin of 52% to 48% to end its 43 years long EU membership, pursuant to a referendum on June 23, 2016. Although in the short-term Brexit may negatively impact India’s trade and investment, it opens up significant long-term opportunities for India.
Opportunities for India
1) Free Trade Agreements (FTA) with UK and EU
India and EU have been negotiating the Bilateral Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA) since 2007, covering trade in merchandise, services, and investment. This is yet to reach a conclusion. However, post-Brexit, UK will necessarily be excluded from BTIA. Among EU countries, while Germany is India’s largest trade partner, UK stands to be India’s third-largest trade partner and biggest importer of goods. Moreover, India has had a trade surplus with UK in the past three years. It is thus crucial for India to have a first mover advantage by executing a bilateral trade agreement with UK encompassing goods, services and technology.
Furthermore, after losing access to the single market, UK will need to independently navigate global (and EU) tariffs and non-tariff barriers including standards, regulations or rules of origin. Relying solely on World Trade Organization (WTO) rules to enhance trade would not remove trade barriers. UK would therefore mainly depend on independent trade deals. Also, with 50 trade agreements between EU and other countries ceasing to apply to UK and after losing EU’s market, UK would want to develop trade relations with emerging markets like India. This strengthens India’s negotiating position. For UK, India is an attractive trade partner, given its high proportion of skilled working-age population and high growth rate. This strengthens the possibility of an FTA between UK and India and presents a significant opportunity for India’s financial and small and medium-sized enterprises (SME) sectors.
UK and India share complementary interests. An FTA would enhance Indian exports of garments, textiles, machinery and instruments to UK, and Indian imports of engineering goods, spirits, beverages, etc. from UK. Similarly, trade in services of Information Technology (IT) and banking would also benefit. UK was the biggest investor in India among the G-20 nations in 2015, while India represents the third-largest source of foreign direct investment (FDI) in Britain. An FTA can lead to greater trade and investment between the two countries.
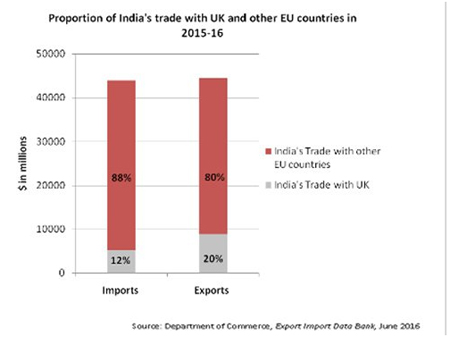
(Proportion of India’s trade with UK and other EU countries in 2015-16.)
Moreover, EU and India would emerge as strong trade partners through enforcement of BTIA. EU is India’s largest trading partner accounting for approximately 13% of its total world trade, while India is EU’s 10th largest trading partner. India is reliant on EU for machinery, nuclear reactors, optical and photo equipment, aircraft, etc. On the other hand, EU’s top imports from India include mineral fuels, oil, distillation products, organic chemicals, textiles, etc. The key sectors of trade in services between the two are sea and air transport, computer and information, financial and banking services.
Indian exports of industrial, agricultural and pharmaceutical products to EU have been hampered by issues concerning Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures, Technical Barriers to Trade and other Non-tariff Barriers. Despite several rounds of negotiations, BTIA has failed to conclude. Access to EU markets was a key driver for Indian companies to invest in UK. With Brexit, UK would no longer remain India’s gateway into Europe. It therefore, becomes even more important for India to conclude BTIA negotiations to access other EU countries.
However, one of the hurdles in the conclusion of these negotiations is EU’s demand for reduction in India’s tariff rates. While EU’s average MFN applied tariff rate is approximately 4.3%, India has an average MFN applied tariff rate of 13.3%. A lowering of tariffs may increase trade with EU, but for India, this may mean more imports than exports, increasing India’s trade deficit. However, it is crucial to evaluate other positive impacts resulting from increased imports such as increase in India’s industrial growth and as a result, export growth.
2) Rise in cheaper imports from UK
Currently, India’s highest imports from EU countries come from Germany. However, with the depreciation of the pound post-Brexit, high quantity of British goods would be available for cheaper prices to the Indian consumer.
Negative impacts
Indian Exports: In the short-term, due to depreciation of the pound, imports into UK would be costlier, which would adversely affect Indian exports, worsening India’s overall trade deficit. However, given the increase in Indian exports to emerging markets, this is not a major threat to India.
Indian companies in UK: Indian IT services companies that have exposure to UK and EU markets and companies based in UK would face several challenges. The depreciation in pound would affect their earnings in rupee terms and a possible increase in tariff barriers would result in increased trading costs. Moreover, there will be increase in operation and compliance costs.
Brexit would possibly lead to bilateral agreements of UK and EU with India. The precise impact of India’s FTAs with UK and EU on its trade balance cannot be known with certainty. However, the FTAs would certainly lead to a rise trade volumes for India. This would result in greater investment in India, lower prices of goods, more competition and greater variety for consumers. There is a possibility that the long-term benefits of Brexit would outweigh the short-term costs for India.
Disclaimer by the authors: This article has been authored by SuhailNathani, who is a Partner and Sanjay Notani, who is a Partner at Economic Laws Practice (ELP), Advocates & Solicitors. The information provided in the article is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal opinion or advice. Readers are requested to seek formal legal advice prior to acting upon any of the information provided herein.
(Source:-http://www.financialexpress.com/economy/trade-impact-of-brexit-on-india-opportunities-and-negatives/357774/ dated 25.08.2016)
|
BACK |
Merchandise exports in India on the rise
|

The merchandise exports from the country have registered an increase of 1.27 percent in Dollar terms (6.72 percent in Rupee terms) in June 2016 compared to the same month of the previous year.
The details of key efforts made by Government for increasing exports are as follows:
- The New Foreign Trade Policy (2015‐20) was announced on 1st April, 2015 with a focus on supporting both manufacturing and services exports and improving the ‘Ease of Doing Business’.
- In the light of the major challenges being faced by Indian exporters in the backdrop of the global economic slowdown, the envisaged revenue outgo under MEIS was increased from Rs. 18000 Crore to Rs. 21000 Crore in October 2015 with accompanying enhancement in benefits on certain products and inclusion of certain additional items. On 04.05.2016, the Government has extended the market coverage to all countries in respect of 2787 lines. Hence Landing Certificates shall not be required under MEISw.e.f 04.05.2016. This step has been taken as part of ‘Ease of Doing Business’ and reduction of Transaction Cost of exporters. Accordingly, revenue foregone under the scheme has been revised from Rs.21000 Crore per annum to Rs.22,000Crore per annum.
- The Government is implementing the NiryatBandhu Scheme with an objective to reach out to the new and potential exporters including exporters from Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) and mentor them through orientation programmes, counselling sessions, individual facilitation, etc., on various aspects of foreign trade for being able to get into international trade and boost exports from India.
- By way of trade facilitation and enhancing the ease of doing business, Government reduced the number of mandatory documents required for exports and imports to three each, which is comparable with international benchmarks. The trade community can file applications online for various trade related schemes. Online payment of application fees through Credit/Debit cards and electronic funds transfer from 53 Banks has been put in place.
- Further, the Government continues to provide the facility of access to duty free raw materials and capital goods for exports through schemes like Advance Authorisation, Duty Free Import Authorization (DFIA), Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) and drawback / refund of duties.
This information was given by the Minister of State (Independent Charge) in the Ministry of Commerce & Industry Smt. NirmalaSitharaman in a written reply in RajyaSabha today.
(Ref.http://www.thehansindia.com/posts/index/Business/2016-07-28/Merchandise-exports-in-India-on-the-rise-/245218 dated 29.07.2016)
|
BACK |
Dia Okays Trade Treaty
|

Indian Prime Minister NarendraModi chaired a cabinet meeting to approve the India-Cambodia bilateral investment treaty. Reuters
The Indian-Cambodia bilateral investment treaty (BIT) was approved on Wednesday by the Indian government in a move to boost and protect trade and investment between the two countries.
According to the statement from the Cabinet Secretariat of India, Wednesday’s cabinet meeting chaired by Prime Minister NarendraModi approved the BIT to encourage each country to create favorable conditions for investors and to promote and protect investments “with the objective of increasing bilateral investment flow.”
Though Cambodia’s Ministry of Commerce had yet to receive formal notification, from the Indian government, of the BIT approval, it, however, welcomed it.
SoengSophary, spokeswoman of the Ministry of Commerce, said the BIT was important to open markets between both India and Cambodia.
“I actually haven’t seen the treaty [approved by the Indian government]. But I am confident it will be good for our countries and it will build trust among businessmen and investors,” said Ms. Sophary.
Both the Indian embassy and Indian Chamber of Commerce in Cambodia did not reply to emails sent by Khmer Times.
According to a report from the Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry, bilateral trade with Cambodia totaled about $160 million in 2014-2015, an increase of about four percent from $154 million in 2013-2014.
Cambodia exported footwear, rubber, fruit and nuts, lime, cement, salt and precious stones to India. Indian exports to Cambodia comprised pharmaceutical products, cotton and man-made fibers, leather, vehicles and plastic, according to the report.
Since 2012, Prime Minister Hun Sen has been pushing for direct air links between Cambodia and India in a bid to boost trade, tourism and investment. That, however, is yet to materialize.
Bilateral trade between Cambodia and India remains small, but the government is pushing for more investment from the world’s second most populous nation.
India-Cambodia relations go back to the first century AD when Hindu and Buddhist religious and cultural influences emanated out of India to various parts of Southeast Asia.
The pervading influence of Hinduism, Buddhism and Indian architecture are borne out by the magnificent structures at Angkor Wat, Angkor Thom, Bayon, Ta Phrom and other religious and historical sites in Cambodia.
(Ref.http://www.khmertimeskh.com/news/27804/india-okays-trade-treaty/ dated 29.
07.2016)
|
BACK |
India will become the start-up destination of the world: Sitharaman
|

The Ministry of Commerce and Industry on Thursday organised a meeting with stakeholders of 30 up-and-coming startups to discuss the key challenges faced by them.
Prominent faces in budding startups were seen at the meet like Paytm’s Vice President Sudhanshu Gupta, Ola’s Senior Director AnandSubramanium, Suraj Saharan, Co-founder of Delhivery, Nykaa.com’s CFO Sachin Parikh, AbhirajBhal, Co-founder of UrbanClap, AnuAcharya, CEO of Mapmygenome, and Rivi Varghese, CEO and Co-founder of CustomerXPs.
“This is the first in a series of dedicated meetings that the Government will hold to have all stakeholders of the Startup ecosystem on board in making India one of the best Startup destinations in the world,” Minister of Commerce, NirmalaSitharaman said in a statement.
The stakeholders raised issues of IPR pendency period, lack of prompt response from incubators for issuing recommendation letters, complicated paper work involved in all government compliances, tedious import/export procedures, need for clear definition of Aggregators under the Service tax among many others.
The government responded that IPR offices have been enhanced considerably in the last six months which will reduce the time taken for examination of patent applications to 18 months by March 2018 compared to over five years now.
“The Startup India initiative is designed to foster innovation, create jobs and facilitate investment. Government is committed to make this initiative a scalable reality and to provide an environment for our Startups to thrive in,” the Ministry said in a statement.
The Ministry also stated time taken for examination of trademark applications will become one month by March 2017.
“The patent applications of Startup are now eligible for expedited examination and reduced fee as per the revised patent rules.
In addition Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion (DIPP) has provided a panel of facilitators who will provide free of cost facilitation to Startups for filing patent applications,” Secretary DIPP said in a statement.
In recent news, Start-up India Hub, an initiative by Prime Minister Modi’s government had reported 12,290 queries that were solved in a matter of 3 months.
Suggestions by Startups
- Tax declaration online: The stakeholders mentioned the difficulties faced by them in interstate movement of goods. For this they suggested that all the states should be asked to take the declarations online and receive taxes online.
- No more manual registers: They also suggested that maintaining manual registers for compliance under labour laws should be done away with.
- Maintaining compliance checklist: Another suggestion by them was that all startups should have a checklist for all the state and central compliances on the Startup India portal, a discussion forum to be evolved for all the stakeholders of the Startup ecosystem to exchange ideas and companies should be asked to spend more on Startups as part of CSR activities.
- Exemption from turnover and experience critera: They also suggested that, banks should also be asked to exempt the Startups from turnover and experience criteria to enable them to participate in the procurement process.
- Ease of procuring credit: They also mentioned that access of credit through banks should be simplified and the time taken should also be reduced. For easier compliance towards various rules and regulations they suggested that a handbook should be prepared and put on public domain.
Government initiatives
The government concluded the meet stating that the government will take up these initiatives to help startups.
- The details of the compliances of Central and State laws expected of a Startup would be posted on the Startup India portal.
- DIPP would take up with the concerned ministries/regulator the various issues raised by the startups pertaining to them.
- Secretary, DIPP promised to facilitate the meeting of various Startups with the concerned departments, so that Startups can take up their issues directly with them.
- DIPP would explore the possibility of developing an app which would enable Startups to know which subject relates to which ministry or regulator.
- The Department would also prepare a handbook to guide Startups on various compliances and the processes involved.
(Ref. http://www.zeebiz.com/small-business/news-india-will-become-the-start-up-destination-of-the-world-sitharam-4287 dated 30.07.2016)
|
BACK |
Russia plans new law for specialty chemicals sector
The Russian government and national Parliament, the State Duma, have started the design of a new federal law that will focus on the regulation of the domestic speciality chemicals industry, writes Eugene Gerden. The as yet unnamed plan is expected to be adopted in October and is aimed at providing impetus for the industry’s further development.
According to Sergey Tsyb, Russia’s deputy minister of industry and trade, who has overall responsibility for the sector, the adoption of the new law, which is exclusively dedicated to speciality chemicals, will be a historically important decision for the industry. Since the collapse of the USSR, the sector’s development has been held back by the lack of a legislative base or its own federal law, with a large number of legislative acts regulating it that sometime contradicted each other.
According to state plans, a particular role in the development of the Russian speciality chemicals industry will be assigned to the country’s leading petroleum and petrochemical companies, which operate Russia’s rich raw materials bases and have all the necessary conditions for the establishment of the domestic production of speciality chemicals.
The new law will regulate the implementation of ambitious state plans, which involve establishing the production of up to 800 different speciality chemical products in Russia during the next few years. The government plans for chemicals to rise from 1.3% of GDP to 2%, with imports falling from 43% of the total to 28% and exports rising from 22% to 45%.
Tsyb added that the adoption of the new federal law should speed up the implementation of the recently announced state plans for the establishment of a new all-Russia centre of speciality chemicals on the basis of the state defence corporation Rostec. The new centre is intended to unite several R&D facilities and production plants focusing on speciality chemical production.
(Ref.http://www.specchemonline.com/news/russia-plans-new-law-for-speciality-chemicals-sector dated 01.08.2016)
|
BACK |
Ministry of Chemicals and Petrochemicals implements PCPIR policy to boost manufacturing
|

New Delhi, July 29 (KNN) With the view to promote investments, boost manufacturing and generate employment, Ministry of Chemicals and Petrochemicals is implementing the Petroleum Chemical and Petrochemical Investment Region Policy (PCPIR).
Substantial investments by upstream Anchor Units in the Refinery and Cracker Segments are envisioned to lead to other investments in the chemical and petrochemical downstream sectors and ancillary industries, said an official release.
Government of India has approved setting up of four PCPIRs in the States of Andhra Pradesh (Vishakhapatnam - Kakinada), Gujarat (Dahej), Odisha (Paradeep) and Tamil Nadu (Cuddalore - Nagapattinam). The fully operational PCPIRs envisage investment of Rs. 7.63 lakh crore and 33.85 lakh job opportunities. No other PCPIR is proposed at present.
The information was given by the Minister of state of Chemicals and Fertilizers Mansukh L. Mandaviya in a written reply to the RajyaSabha today. (With PIB Inputs)
(Ref. http://knnindia.co.in/news/newsdetails/sectors/ministry-of-chemicals-and-petrochemicals-implements-pcpir-policy-to-boost-manufacturing dated 30.07.2016)
|
BACK |
Class 3 Flammable liquids
Liquids, or mixtures of liquids, or liquids containing solids in solution or suspension which gives off a flammable vapour at or below 60°C closed-cup test is classified as flammable liquid in transport regulations. Flashpoint is the lowest temperature of the liquid at which its vapour forms an ignitable mixture with air.
GHS & Transport Regulations Classifies flammable liquid under below Categories
Criteria |
GHS Category |
Transport Regulations |
Flash point < 23 °C and initial boiling point ≤35 °C |
1 |
Packing Group I |
Flash point < 23 °C and initial boiling point > 35 °C |
2 |
Packing Group II |
Flash point ≥23 °C and ≤60 °C |
3 |
Packing Group III |
Flash point > 60 °C and ≤93 °C |
4 |
Combustible Liquid |
Packing group assist the shipper to select the right package.
Certain flammable liquid which are viscous, such as paints, enamels, varnishes, adhesives and polishes, having a flashpoint of less than 23°C may be placed in packing group III provided it meets the conditions laid down in part III, chapter 32.3, of the United Nations Manual of Tests and Criteria, which includes:
- the viscosity, expressed as the flowtime in seconds
- the closed-cup flashpoint
- a solvent separation test, and
- the capacity of the receptacle used does not exceed 30 ℓ and no additional risk of corrosivity or toxicity.
Flammable liquid which has flashpoint of more than 35°C may be exempted from provisions of IMDG Code if it does not sustain combustion. The criteria for a liquid to be not sustaining combustion is if;
- they have passed the suitable combustibility test (see the Sustained Combustibility Test prescribed in part III, 32.5.2 of the United Nations Manual of Tests and Criteria); or
- their fire point according to ISO 2592:1973 is greater than 100°C; or
- they are water-miscible solutions with a water content of more than 90%, by mass.
Flammable Liquid includes
- liquids offered for transport at temperatures at or above their flashpoint;
Example:Benzoic Acid Molten has a flashpoint of 121 Deg C and its melting point is 122 Deg C, When transported as Molten the cargo temperature is greater than 122 Deg C which is higher than its flashpoint.
- substances transported or offered for transport at elevated temperatures in a liquid state, which give off a flammable vapour at temperatures equal to or below the maximum transport temperature.
Example: Bitumen
While filling flammable liquid into packages the filler must ensure to take measures to prevent dangerous electrostatic discharge and must strictly adhere to the degree of filling for tanks.
Flammable liquid may have additional risk of toxicity or corrrosivity. For those liquids, having multiple hazards and are not listed by name in IMDG Code the shipper must classify them according to part 2.0 & 2.3 of the Code taking great attention to precedence of hazards, Classification of substances, mixtures and solutions with multiple hazards.
Class 3 also includes liquid desensitized explosives which are explosive substances dissolved or suspended in water or other liquid substances, to form a homogeneous liquid mixture to suppress their explosive properties. Follwing are the entries in IMDG Code for liquid desentisized explosives:
- UN No. 1204 NITROGLYCERIN SOLUTION IN ALCOHOL with not more than 1% nitroglycerin
- UN No. 2059 NITROCELLULOSE SOLUTION, FLAMMABLE with not more than 12.6% nitrogen, by dry mass, and not more than 55% nitrocellulose
- UN No. 3064 NITROGLYCERIN SOLUTION IN ALCOHOL with more than 1% but not more than 5% nitroglycerin
- UN No. 3343 NITROGLYCERIN MIXTURE, DESENSITIZED, LIQUID, FLAMMABLE, N.O.S. with not more than 30% nitroglycerin, by mass
- UN No. 3357 NITROGLYCERIN MIXTURE, DESENSITIZED, LIQUID, N.O.S. with not more than 30% nitroglycerin, by mass
- UN No. 3379 DESENSITIZED EXPLOSIVE, LIQUID, N.O.S.
Emergency Response on board ships
For carriage on board ships flammable liquids are permited to be loaded on or under deck as per the stowage category assigned in IMDG Code for a particular UN Number with the assigned packing group and as per Document of compliance for ships carrying dangerous goods under the provisions of regulation II-2/19 of the 1974 SOLAS Convention, as amended.
In Document of Compliance permitted stowage in under deck spaces are separately listed for
- Class 3 Flashpoint< 23°C
- Class 3 Flashpoint ≥ 23°C to ≤ 60°C
- Class 6.1 liquids Flashpoint< 23°C
- Class 6.1 liquids Flashpoint ≥ 23°C to ≤ 60°C
- Class 8 liquids Flashpoint< 23°C
- Class 8 liquids Flashpoint ≥ 23°C to ≤ 60°C
Certain flammable liquids will float on water and if firefighting personnel direct the water jet on to the liquid it may result in spreading of fire further creating greater danger. During fire heated flammable liquid will release vapours which will burn with explosive effect. Firefighting personnel must stay in well protected area and use water spray to cool down the temperature of the liquid and vapour.
Vaporized flammable liquid may result in devastating Vapour Cloud Explosion. Some of the flammable liquids are corrosive to skin or to ships hull. Long term toxic effects are not classified and labelled hence ships personnel must take great care while dealing with spillage or fire involving flammable liquid. It is highly recommended to use self-contained breathing apparatus while dealing with flammable liquid incidents and accidents on board vessel.
General Comments for fighting fire of Non-Water Reactive Flammable Liquids:
- Cargoes in tanks exposed to heat may explode suddenly in or after a fire situation by a Boiling Liquid-Expanding Vapour Explosion (BLEVE).
- Keep tanks cool with copious quantities of water.
- Fight fire from a protected position from as far away as possible.
- Stop leakage or close open valve if practicable.
- Flames may be invisible.
Container fire on deck: Cool burning transport units and nearby cargo exposed to the fire with copious quantities of water.
Container fire under deck: Stop ventilation and close hatches. Use cargo space fixed fire-extinguishing system. If this is not available, create water spray using copious quantities of water.
|
BACK |
REMINDER - Inviting Pre-Budget Proposals for the year 2017-18
|
EPC/LIC/EU |
1st August, 2016.
|
| ALL COSMETICS MEMBERS OF THE COUNCIL
|
|
G/TBT/N/EU/387 TBT notification issued by EU on new Hair Dye Substances
|
|
Dear Members,
EU has issued a TBT Notification No G/TBT/N/EU/387 on new hair dye substances. The European Commission has issued this notification concerning authorization of Six New Hair Dye Substances.
This draft Commission Regulation aims at authorising six hair dye substances for use in products intended to colour eyelashes and at regulating, in the context of the assessment strategy for hair dyes, ten newly assessed hair dye substances in Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009. The proposed maximum authorised concentrations are based on the latest opinions of the Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety (SCCS) on these substances.
The substances are as follows:
Ethanol, 2,2'-[(2-nitro-1,4-phenylene)diimino]bis-(9CI)
1,4-Benzenediamine, 2-methyl- 2,5-Diaminotoluene sulphate
1-Methyl-2,6-bis-(2-hydroxyethylamino)-benzene
2,4,5,6- Tetraaminopyrimidine sulphate
3-(2-Hydroxyethyl)- p-phenylenediammonium sulphate
2-Aminopyridin-3-ol
1,3-benzenediol, 2- methyl
4-Aminophenol "EN-US"
Di-[2-[4-[(E)-2-[4- [bis(2- hydroxyethyl)aminophenyl]vinyl]pyridin-1-ium]- butanoyl] aminoethyl]dis ulfanyl dichloride
Di-[2-[4-[(E)-2-[2,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl]vinyl] pyridinin-1- ium]butanoyl]aminoethyl ]disulfanyl dichloride
1H-Pyrazole-4,5- diamine, 1-hexyl-, sulfate (2:1)
4-Hydroxy-2,5,6- triaminopyrimidine sulfate
2-[(3- aminopyrazolo[1,5- a]pyridin-2- yl)oxy]ethanol hydrochloride
Phenol, 3-amino-2,6-dimethyl
2-Naphthalenaminium,8-[(4-amino-3-nitrophenyl)azo]-7-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethyl-,chloride
3-Amino-7-(dimethylamino)-2-methoxyphenoxazin-5-ium chloride
The EU authorities are of view that, the focus of this notification is protection of human health and safety.
You are kindly requested to take note of the same. For more details, please also refer the TBT notification and regulations attached in this mail.
Thanking You,
Yours faithfully,
( S.G.BHARADI )
EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR
CHEMEXCIL
Encl :
http://chemexcil.in/uploads/files/(20160714)_eu387.pdf
http://chemexcil.in/uploads/files/16_2774_00_e.pdf
http://chemexcil.in/uploads/files/16_2774_01_e.pdf
|
BACK
|
Relief in Average Export Obligation in terms of Para 5.19 of Hand Book of Procedures of FTP 2015-20.
| EPC/LIC/DGFT/EPCG/EO |
2nd August, 2016. |
| ALL MEMBERS OF THE COUNCIL |
|
Relief in Average Export Obligation in terms of Para 5.19 of Hand Book of Procedures of FTP 2015-20.
|
|
Dear Members,
We would like to inform you that the O/o DGFT New Delhi has issued Policy Circular no. 01/2015-20 dated 26/07/2016 regarding relief in Average Export Obligation for EPCG authorisation holders in terms of Para 5.19 of Hand Book of Procedures of FTP 2015-20.
As you might be aware, Para 5.19 of the Hand Book of Procedures of FTP 2015-20 permits re-fixation of Annual Average Export obligation, in case the export in any sector/ product group declines by more than 5%. This implies that the sector/product group which witnessed such decline in 2015-16 as compared to 2014-15, would be entitled to such a relief.
A list of such product groups showing the percentage decline in exports during 2015-16 as compared to 2014-15 is Annexed with above circular . As per the circular, All DGFT RA's have been requested to re-fix the annual average export obligation for EPCG Authorizations for 2015-16 accordingly. Reduction, if any, in the EO should be endorsed in the licence file of RA and also in the Amendment Sheet to EPCG authorisation holder.
Members are requested to take note of same. For further details and list of sectors, Policy Circular no. 01/2015-20 dated 26/07/2016 may be downloaded from the below link-
http://dgft.gov.in/Exim/2000/CIR/CIR16/pc01_2017.pdf
Thanking You,
Yours faithfully,
(S.G.BHARADI
EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR
|
BACK
|
REMINDER - Inviting Pre-Budget Proposals for the year 2017-18
|
EPC/LIC/EGYPT |
10 th August 2016
|
|
ALL MEMBERS OF THE COUNCIL
|
|
Issues faced by Indian exporters while doing business with Egypt
|
|
Dear Members,
The Council has received communication from the Department of Commerce, WANA Section, MOC&I regarding issues/problems, if any, being faced by Indian exporters while doing business with Egypt.
Kindly note that, a visit of high level delegation from Egypt is planned for India in the next few weeks. The Department of Commerce has commenced an exercise to prepare the agenda of items/ issues which need to be addressed.
In this regard, member-exporters are requested to highlight issues which are required to be taken-up with the Egyptian side. The same may be sent at the earliest by 16 August 2016 on our e-mail id’s- deepak.gupta@chemexcil.gov.in & balani.lic@chemexcil.gov.in .
Your timely feed-back will be appreciated..
Thanking You,
Yours faithfully,
( S.G.BHARADI )
EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR
CHEMEXCIL
|
BACK
|
REMINDER - Inviting Pre-Budget Proposals for the year 2017-18
|
EPC/LIC/PRE-BUDGET 2017-18 |
10 th August 2016
|
| ALL MEMBERS OF THE COUNCIL
|
|
Inviting Pre-Budget Proposals for the year 2017-18
|
|
Dear Members,
The Council has received intimation from the Deputy Secretary, Trade Finance Section, Dept. of Commerce regarding commencement of the Pre-Budget Exercise for the forthcoming year 2017-18.
In this regard, export-related proposals are invited for consideration by the Department of Commerce in the attached pro-forma format. Members are also requested to follow the guidelines specified in the attached Memorandum dated 1 st August 2016 received from the Trade Finance Section, Department of Commerce.
The budget proposals be sent taking into consideration following aspects:
-
Budget Proposals should be complete in all respects, properly categorized and HS Codes for each commodity must be provided.
- Justification given in favour of the proposals shall be restricted to 300 words and annexure should be used, if necessary.
- Issues discussed year after year but never agreed to, may not be raised again.
Members are requested to kindly forward their proposals in the specified pro-forma format latest by 25th August 2016 on our e-mail ids deepak.gupta@chemexcil.gov.in& balani.lic@chemexcil.gov.in.
Your timely responses shall be appreciated as the Council has to examine the proposals and collate them for onward submission to Department of Commerce by timeline of 30 th August, 2016. As per the directive of the memo, proposals received by DOC after 30 th August 2016 shall not be considered, so we solicit your co-operation in this regard.
Thanking You,
Yours faithfully,
( S.G.BHARADI )
EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR
CHEMEXCIL
Encl : Pre-Budget Memo 2017-18
|
BACK
|
|

